4. Installation¶
Note
These instructions assumes Ubuntu 14 and CentOS 7
4.1. EDGE Installation¶
Note
A base install is ~12GB for the code base and ~500GB for the databases.
Please ensure that your system has the essential software building packages. installed properly before proceeding following installation.
Download the codebase, databases and third party tools.:
## Codebase is ~207Mb and contains all the scripts and HTML needed to make EDGE run wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/2.x/edge_2.3_main.tgz ## Third party tools is ~2.8Gb and contains the underlying programs needed to do the analysis wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/2.x/edge_2.3_thirdParty_softwares.tgz ## Pipeline database is ~17Gb and contains the other databases needed for EDGE wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_pipeline_databases.tgz ## BWA index is ~41Gb and contains the databases for bwa taxonomic identification pipeline wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_bwa_index.tgz ## HOST genomes BWA index is ~41Gb for Host removal, including human, bacteria, phiX, viruses, invertebrate vectors of human pathogens wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_HostIndex.tgz ## NCBI Genomes is ~21Gb and contain the full genomes for prokaryotes and some viruses wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_NCBI_genomes.tgz ## GOTTCHA database is ~16Gb and contains the custom databases for the GOTTCHA taxonomic identification pipeline wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_GOTTCHA_db.tgz ## Amplicon database is ~78Mb and contains the databases for Qiime 16s and 18s ITS pipeline wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_amplicons_db.tgz ## NT database is ~25Gb and contains the NCBI nt database for contig identification wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_nt_20160426.tgz ## ShortBRED database is ~27Mb and contains the databases used by ShortBRED for virulence factors and read based antibiotic resistance analysis wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_ShortBRED_Database.tgz ## Diamond database is ~16Gb and contains the databases from RefSeq for protein based taxonomic identification wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_diamond_db.tgz ## MetaPhlAn2 database is 1.1Gb contains the databases used for the MetaPhlAn2 taxonomic identification pipeline wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_metaphlan2DB.tgz (Optional) ## Other Host bwa index ~18Gb for host removal, including pig, sheep, cow, monkey, hamster. and goat. wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/DB/edge_dev_otherHostIndex.tgz ## GOTTCHA2 databases are 27Gb and ~1Gb and contains the custom databases for the GOTTCHA2 taxonomic identification pipeline wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_GOTTCHA2_bac_db.tgz wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_GOTTCHA2_virus_db.tgz ## For machine with < 32Gb memory, we suggest to use the smaller BWA index (~14Gb) and contains the databases for bwa taxonomic identification pipeline wget -c https://edge-dl.lanl.gov/EDGE/dev/edge_dev_bwa_mini_index.tgz
Warning
Be patient; the database files are huge.
Unpack main archive:
tar -xvzf edge_dev_main.tgz
Note
The main directory, edge_dev, will be created.
Create a link from edge to that directory:
ln -sf edge_dev edge
Unpack the third party software into main directory (edge):
tar -xvzf edge_dev_thirdParty_softwares.tgz -C edge/
Note
You should see a thirdParty directory inside the edge directory.
5 Unpack the databases:
# unpack databases
tar -xvzf edge_dev_pipeline_databases.tgz
tar -xvzf edge_dev_GOTTCHA_db.tgz
tar -xzvf edge_dev_bwa_index.tgz
tar -xvzf edge_dev_NCBI_genomes.tar.gz
tar -xzvf edge_dev_amplicons_db.tgz
tar -xzvf edge_dev_nt_20160426.tgz
tar -xvzf edge_dev_ShortBRED_Database.tgz
tar -xvzf edge_dev_HostIndex.tgz
tar -xvzf edge_dev_diamond_db.tgz
tar -xvzf edge_dev_metaphlan2DB.tgz
Note
At this point, you should see a database directory and the edge directory.
Create the symlink from edge to the database directory:
ln -s `pwd`/database edge/database
Note
This will keep the database directory outside of the edge install location. Should you need to reinstall the code base you will not need to redownload/install the databases.
Installing pipeline:
cd edge ./INSTALL.sh
Note
When installing JBrowse, it may require internet connection.
Note
If the machine is shared and used with others, the system installed tools version may not be compatible with EDGE. In this case, we would suggest to use force option ./INSTALL.sh force to install all list tools locally.
It will install the following depended tools.
Assembly
- idba
- spades
- megahit
- long_read_assembly
- racon
Annotation
- prokka
- RATT
- tRNAscan
- barrnap
- BLAST+
- blastall
- phageFinder
- glimmer
- aragorn
- prodigal
- tbl2asn
- ShortBRED
Alignment
- hmmer
- infernal
- bowtie2
- bwa
- mummer
- RAPSearch2
- diamond
- minimap2
Taxonomy
- kraken
- metaphlan2
- kronatools
- gottcha
- gottcha2
Phylogeny
- FastTree
- RAxML
Utility
- FaQCs
- bedtools
- R
- GNU_parallel
- tabix
- JBrowse
- bokeh
- primer3
- samtools
- bcftools
- sratoolkit
- ea-utils
- omics-pathway-viewer
- NanoPlot
- Porechop
- Rpackages
Perl_Modules
- perl_parallel_forkmanager
- perl_excel_writer
- perl_archive_zip
- perl_string_approx
- perl_pdf_api2
- perl_html_template
- perl_html_parser
- perl_JSON
- perl_bio_phylo
- perl_xml_twig
- perl_cgi_session
- perl_email_valid
- perl_mailtools
Python_Packages
- Anaconda2
- Anaconda3
Pipeline_Tools
- DETEQT
- reference-based_assembly
- PyPiReT
- Restart the Terminal Session to allow $EDGE_HOME to be exported.
Note
After running INSTALL.sh successfully, the binaries and related scripts will be stored in the ./bin and ./scripts directory. It also writes EDGE_HOME environment variable into .bashrc or .bash_profile.
4.1.1. Testing the EDGE Installation¶
After installing the packages above, it is highly recommended to test the installation:
> cd $EDGE_HOME/testData
> ./runAllTest.sh
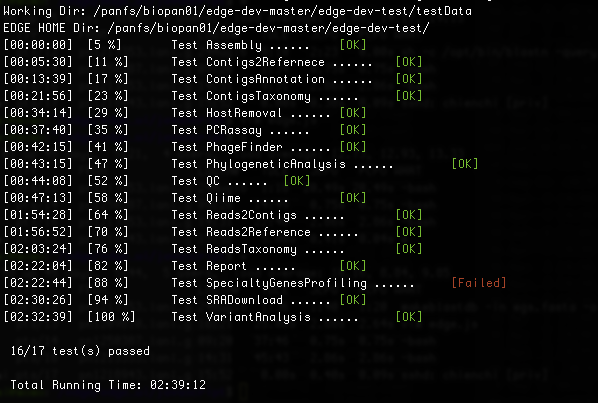
There are 17 module/unit tests which took around 2 hours 14 mins in our testing environments. (64 cores 2.30GHz, 512GB ram with CentOS-7.1.1503 ). You will see test output on the terminal indicating test successes and failures. The Specialty Genes Profiling test will fail in this stage since it requires virulence database imported and configured. You can test it again after database created and configured. Some tests may fail due to missing external applications/modules/packages or failed installation. These will be noted separately in the $EDGE_HOME/testData/runXXXXTest/TestOutput/error.log or log files in each modules. If these are related to features of EDGE that you are not using, this is acceptable. Otherwise, you’ll want to ensure that you have the EDGE installed correctly. If the output doesn’t indicate any failures, you are now ready to use EDGE through command line. To take advantage of the user friendly GUI, please follow the section below to configure the EDGE Web server.
4.1.2. Apache Web Server Configuration¶
Modify/Check sample apache configuration file:
For Ubuntu Double check $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/edge_apache.conf alias directories the match EDGE installation path at line 2,5,6,16,17,29,59. The default is configured as http://localhost/edge_ui/ or http://www.yourdomain.com/edge_ui/ For CentOS Double check $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/edge_httpd.conf alias directories the match EDGE installation path at line 2,5,6,16,17,29,59. The default is configured as http://localhost/edge_ui/ or http://www.yourdomain.com/edge_ui/
Confirm apache/httpd user and groups are edge:
For Ubuntu The user and group can be edited at /etc/apache2/envvars and the variables are APACHE_RUN_USER and APACHE_RUN_GROUP. For CentOS The User and Group on lines 66 and 67 in $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/centos_httpd.conf should be edge ## Make APACHE_RUN_USER have Permission to write > sudo chown -R xxxxx $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/JBrowse/data #(xxxxx is the APACHE_RUN_USER value) > sudo chgrp -R xxxxx $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/JBrowse/data #(xxxxx is the APACHE_RUN_GROUP value)
(Optional) If users are behind a corporate proxy for internet:
Please add proxy info into $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/edge_apache.conf or $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/edge_httpd.conf # Add following proxy env SetEnv http_proxy http://yourproxy:port SetEnv https_proxy http://yourproxy:port SetEnv ftp_proxy http://yourproxy:port
Copy configuration files to the appropriate directories:
For Ubuntu > sudo cp $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/edge_apache.conf /etc/apache2/conf-available/ > sudo ln -s /etc/apache2/conf-available/edge_apache.conf /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/ > sudo cp $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/pangia-vis.conf /etc/apache2/conf-available/ > sudo ln -s /etc/apache2/conf-available/pangia-vis.conf /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/ For CentOS > sudo cp $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/edge_httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/ > sudo cp $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/centos_httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf > sudo cp $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/pangia-vis.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/
(Optional) HTTPS / SSL configuration:
i. Please add redirect conditions into $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/edge_apache.conf or $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/edge_httpd.conf # Add redirect to https RewriteEngine on RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on RewriteRule ^(.*) https://%{SERVER_NAME}$1 [R,L] ii. Use pangia-vis-https.conf instead of pangia-vis.conf For Ubuntu > sudo cp $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/pangia-vis-https.conf /etc/apache2/conf-available/pangia-vis.conf For CentOS > sudo cp $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/pangia-vis-https.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/ iii. Add SSL configuration:: see edge_ssl.conf using letsencrypt (https://letsencrypt.org/) as an example. Please modify it as your environments and copy modified $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/apache_conf/edge_ssl.conf to /etc/httpd/conf.d/ for CentOS or /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/ for Ubuntu.Restart the apache2/httpd to activate the new configuration:
For Ubuntu > sudo service apache2 restart For CentOS > sudo systemctl restart httpd
4.1.3. User Management System Installation: MySQL¶
Note
Setup two temporary environmental variables:
UN=username
PW=password
These will be used when setting up the user management system
Note
If you were using the user management system and are updating from EDGE v1.1 to this version. You only need to run the commands below and continue to install tomcat.:
cd $EDGE_HOME/userManagement
mysql -u $UN -p userManagement
mysql> source update_userManagement_db.sql
Start mysql (if it is not already running):
For Ubuntu > sudo service mysql start For CentOS sudo systemctl start mariadb.service && sudo systemctl enable mariadb.service
Secure mysql:
Note
The root password here is for the mysql root and not the system root.
> sudo mysql_secure_installation
- Enter root password (likely none)
- Set root password? Yes
- Enter new root password.
- Re-enter new root password.
- Remove anonymous users? Yes
- Disallow root login remotely? Yes
- Remove test database and access to it? Yes
- Reload privilege table now? Yes
Create database: userManagement:
> cd $EDGE_HOME/userManagement > mysql -p -u root mysql> create database userManagement; mysql> use userManagement;
Load userManagement_schema.sql:
mysql> source userManagement_schema.sql;
Load userManagement_constrains.sql:
mysql> source userManagement_constrains.sql;
Create an user account and grant all privileges to user:
Note
This is the database user (not an individual account).
Replace with the appropriate values:
username: yourDBUsername password: yourDBPassword
mysql> CREATE USER 'yourDBUsername'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'yourDBPassword'; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON userManagement.* to 'yourDBUsername'@'localhost'; mysql> exit;
4.1.4. User Management System Installation: Tomcat¶
Note
If you were using the user management system and are updating from EDGE v1.1 to this version. You only need continue from step 6.
Configure tomcat basic auth to secure /user/admin/register web service:
Warning
Run this code only once!
Note
The username and password here should be the same as the database user.
Update the values for the username and password accordingly before running the code.
This adds the following to /usr/share/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml or /var/lib/tomcat7/conf/tomcat-users.xml:
<role rolename="admin"/> <user username="yourAdminName" password="yourAdminPassword" roles="admin"/>
For Ubuntu sudo sed -i 's@</tomcat-users>@<role rolename="admin"/>\n<user username="'"${UN}"'" password="'"${PW}"'" roles="admin"/>\n</tomcat-users>@g' /var/lib/tomcat7/conf/tomcat-users.xml For CentOS sudo sed -i 's@<!-- <role rolename="admin"/> -->@<!-- <role rolename="admin"/> -->\n<role rolename="admin"/>\n<user username="'"${UN}"'" password="'"${PW}"'" roles="admin"/>@g' /usr/share/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml
Update inactive timeout to a more reasonable number 4320 min (3 days) from default (30mins) in /var/lib/tomcat7/conf/web.xml or /etc/tomcat/web.xml
Note
This is modifying the following code:
<!-- <session-config> <session-timeout>30</session-timeout> </session-config> -->For Ubuntu sudo sed -i 's@<session-timeout>.*</session-timeout>@<session-timeout>4320</session-timeout>@g' /var/lib/tomcat7/conf/web.xml For CentOS sudo sed -i 's@<session-timeout>.*</session-timeout>@<session-timeout>4320</session-timeout>@g' /usr/share/tomcat/conf/web.xml
Add memory constrains to Java:
Warning
Run this code only once!
Note
This will add the following line to the appropriate file:
JAVA_OPTS=" -Xms256M -Xmx1024M -XX:PermSize=256m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m"
For Ubuntu sudo sed -i 's@#JAVA_OPTS@JAVA_OPTS="-Xms256m -Xmx1024m -XX:PermSize=256m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m"\n#JAVA_OPTS@g' /usr/share/tomcat7/bin/catalina.sh For CentOS sudo sed -i 's@#JAVA_OPTS@JAVA_OPTS="-Xms256m -Xmx1024m -XX:PermSize=256m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m"\n#JAVA_OPTS@g' /usr/share/tomcat/conf/tomcat.conf
Restart tomcat server:
For Ubuntu sudo service tomcat7 restart For CentOS7 sudo systemctl restart tomcat
Copy database connector clients to appropriate lib directory:
For Ubuntu sudo cp mysql-connector-java-5.1.34-bin.jar /usr/share/tomcat7/lib/ sudo chmod 744 /usr/share/tomcat7/lib/mysql-connector-java-5.1.34-bin.jar For CentOS sudo cp mariadb-java-client-1.2.0.jar /usr/share/tomcat/lib/ sudo chmod 744 /usr/share/tomcat/lib/mariadb-java-client-1.2.0.jar
Centos Only: Update the MySQL database driver to be used:
sed -i 's@driverClassName=.*$@driverClassName="org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver"@' $EDGE_HOME/userManagement/userManagementWS.xml
Deploy userManagement to tomcat server:
Note
For CentOS the userManagementWS.xml should have:
driverClassName="org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver"
Please check and confirm this before deploying userManagement.
For Ubuntu sudo rm -rf /var/lib/tomcat7/webapps/userManagementWS sudo cp userManagementWS.war /var/lib/tomcat7/webapps/ sudo rm -rf /var/lib/tomcat7/webapps/userManagement sudo cp userManagement.war /var/lib/tomcat7/webapps/ sudo chmod 755 /var/lib/tomcat7/webapps/*war sudo cp userManagementWS.xml /var/lib/tomcat7/conf/Catalina/localhost/ sudo chmod 744 /var/lib/tomcat7/conf/Catalina/localhost/userManagementWS.xml For CentOS sudo rm -rf /var/lib/tomcat/webapps/userManagementWS sudo cp userManagementWS.war /var/lib/tomcat/webapps/ sudo rm -rf /var/lib/tomcat/webapps/userManagement sudo cp userManagement.war /var/lib/tomcat/webapps/ sudo chmod 755 /var/lib/tomcat/webapps/*war sudo cp userManagementWS.xml /etc/tomcat/Catalina/localhost/ sudo chmod 744 /etc/tomcat/Catalina/localhost/userManagementWS.xml
Modify the username/password in userManagementWS.xml:
For Ubuntu sudo sed -i 's@username=.*$@username="'"${UN}"'"@' /var/lib/tomcat7/conf/Catalina/localhost/userManagementWS.xml sudo sed -i 's@password=.*$@password="'"${PW}"'"@' /var/lib/tomcat7/conf/Catalina/localhost/userManagementWS.xml For CentOS sudo sed -i 's@username=.*$@username="'"${UN}"'"@' /etc/tomcat/Catalina/localhost/userManagementWS.xml sudo sed -i 's@password=.*$@password="'"${PW}"'"@' /etc/tomcat/Catalina/localhost/userManagementWS.xml
Update sys.properties in the userManagement deployment:
Note
Tomcat should automatically unarchive the .war files.
The default configuration is to have the user management system on localhost with email notifications turned off.
Modify the user management sys.properties if you want to change the default behavior.
You will need to copy the sys.properties files to the directory of the userManagement deployment.
For Ubuntu sudo cp $EDGE_HOME/userManagement/sys.properties /var/lib/tomcat7/webapps/userManagement/WEB-INF/classes/sys.properties sudo chmod 744 /var/lib/tomcat7/webapps/userManagement/WEB-INF/classes/sys.properties For CentOS sudo cp $EDGE_HOME/userManagement/sys.properties /usr/share/tomcat/webapps/userManagement/WEB-INF/classes/sys.properties sudo chmod 744 /usr/share/tomcat/webapps/userManagement/WEB-INF/classes/sys.properties
Restart tomcat server:
For Ubuntu sudo service tomcat7 restart For CentOS7 sudo systemctl restart tomcat
Setup admin user:
Note
The script createAdminAccount.pl creates an admin user account for EDGE userManagement.
Update email (-e), First Name (-fn), and Last Name (-ln) appropriately.
It will ask tomcat service username and password (tomcat-users.xml:) before creating EDGE user account (email).
If “HTTP Status 401” error shows, please make sure the tomcat username and password in the first step match with what entered here.
If “HTTP Status 403” error shows, please make sure the tomcat rolename in the first step match with /var/lib/tomcat/webapps/userManagementWS/WEB-INF/web.xml and where the web.xml file existed or not.
Should this script fail, the userManagement is not set up correctly.
perl createAdminAccount.pl -e <email> -fn <first name> -ln <last name>
Enable userManagement in EDGE sys.properties:
Note
See EDGE Configuration below
> sed -i 's@user_management=.*$@user_management=1@g' $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/sys.properties > sed -i 's@edge_user_management_url=.*$@edge_user_management_url=http://localhost/userManagement@g' $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/sys.properties
Optional: configure social (facebook,google,windows live, Linkedin) login function:
- modify $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/javascript/social.js, change apps id you created on each social media.
Note
You need to register your EDGE’s domain on each social media to get apps id. e.g.: A FACEBOOK app needs to be created and configured for the domain and website set up by EDGE. see https://developers.facebook.com/ and StackOverflow Q&A
Optional: configure sendmail to use SMTP to email out of local domain:
edit /etc/mail/sendmail.cf and edit this line:
# “Smart” relay host (may be null) DS
and append the correct server right next to DS (no spaces);
# “Smart” relay host (may be null) DSmail.yourdomain.com
Then, restart the sendmail service
> sudo service sendmail restart
4.1.5. MYSQL Databases CREATION¶
Note
This requires that MySQL is installed and running.
Note
EDGE provides Virulence Factors, Metadata, and Pathogen sql dump files which will be used for Speciality Gene Profling module, Sample MetaData module and Pathogen Detection module, respectively. You will need configure the database info in the $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/sys.properties. See EDGE Configuration below
Change directory into database:
cd $EDGE_HOME/SQLdbfile
Run install script for databases and Grant privilege database user to have access to the databases:
mysql -u root -p mysql> source virulence_db.sql ; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON virulenceFactors.* to 'yourDBUsername'@'localhost'; mysql> create database edgeDB; mysql> use edgeDB; mysql> source edge_db.sql ; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON edgeDB.* to 'yourDBUsername'@'localhost'; mysql> create database pathogens ; mysql> use pathogens; mysql> source pathogen_db.sql ; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON pathogens.* to 'yourDBUsername'@'localhost'; mysql> exit;
Configure Virulence, Metadata and Pathogen Database information:
Edit $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/sys.properties with the appropriate database username and password. # Virluence Factoer database VFDB_dbhost = localhost VFDB_dbport = 3306 VFDB_dbname = virulenceFactors VFDB_dbuser = edge_user VFDB_dbpasswd = edge_user_password ##configure edge pathogen detection 1: with 0: without edge_pathogen_detection=0 pathogen_dbhost=localhost pathogen_dbname=pathogens pathogen_dbuser=edge_user pathogen_dbpasswd=edge_user_password ##configure edge sample metadata option 1: with 0: without edge_sample_metadata=0 edge_dbhost=localhost edge_dbname=edgeDB edge_dbuser=edge_user edge_dbpasswd=edge_user_password
4.1.6. EDGE configuration¶
Note
EDGE system configuration file is $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/sys.proprties. You can edit this file to turn on/off EDGE functions/modules here. (on=1, off=0);
- Add EDGE GUI admin info:
#According to User Management system installation step 11:
edgeui_admin=admin@my.com
edgeui_admin_password=admin
Turn on user management system:
Note
This assumes localhost is the domain. Update the domain as necessary. If user management system is not in the same domain with EDGE.:
edge_user_management_url=http://www.someother.com/userManagement
# If you have User Management system enabled. user_management=1 edge_user_management_url=http://localhost/userManagement
Turn on upload function:
user_upload=1 user_upload_maxFileSize='5gb'
Turn on project intermediate files clean up:
#Clean up old bam/sam/fastq/gz files (based on file age) in project directories edgeui_proj_store_days=10
Set up the archive directory:
#The archive space is for offload the main computational disk space edgeui_archive=/path/to/archive_SPACE
Turn on Social Login function:
#If you have User Management system installation step 18 done. user_social_login=1
Turn on job submission for SGE/UGE cluster environment:
Note
make sure the user/apache user running EDGE is a cluster user.
qconf -suserl to check cluster user list
#Configure cluster system 1: with 0: without
cluster=1
## sge environment configuration
sge_bin=/cm/shared/apps/sge/2011.11p1/bin/linux-x64
sge_root=/cm/shared/apps/sge/2011.11p1
sge_cell=default
## edge job submission configuration
cluster_job_notify=edge@yourdomain.com
cluster_job_prefix=EDGE_pipeline_
cluster_qsub_options=
cluster_job_resource=h_vmem=6G -pe smp <CPU> -binding linear:<CPU/2>
cluster_job_max_cpu=64
4.2. Configure SELinux on CentOS¶
Warning
This is not complete.
Install semanage (if not already installed):
> sudo yum install -y policycoreutils-python setroubleshoot
Allow httpd to access $EDGE_HOME, the databases, and read/write to the EDGE_input/EDGE_output:
> sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "$EDGE_HOME(/.*)?" > sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "$EDGE_HOME/database(/.*)?" > sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "$EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/EDGE_input(/.*)?" > sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "$EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/EDGE_output(/.*)?"
Allow httpd to execute cgi-scripts in $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/cgi-bin/:
> sudo semanage boolean -m --on httpd_enable_cgi > sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_script_exec_t "$EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/cgi-bin(/.*)?"
Allow httpd to connect to mysql database:
> sudo semanage boolean -m --on httpd_can_network_connect_db
Optional: Allow httpd to work with nfs and send mail:
> sudo semanage boolean -m --on httpd_use_nfs > sudo semanage boolean -m --on httpd_can_sendmail
REQUIRED: Apply the rules:
> sudo restorecon -R $EDGE_HOME > sudo restorecon -R $EDGE_HOME/database/ > sudo restorecon -R $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/EDGE_input/ > sudo restorecon -R $EDGE_HOME/edge_ui/EDGE_output/
4.3. EDGE Docker image¶
EDGE has a lot of dependencies and can (but doesn’t have to) be very challenging to install. The EDGE docker gets around the difficulty of installation by providing a functioning EDGE full install on top of offical CentOS Base Image(7.3.1611). You can find the image and usage at docker hub. We would recommend to use Docker container for easy update in the future.
4.4. EDGE VMware/OVF Image¶
You can start using EDGE by launching a local instance of the EDGE VM. The image is built by VMware Fusion v8.5.0. The pre-built EDGE VM is provided in Open Virtualization Format (OVA/OVF) which is supported by major virtualization players, such as VMware / VirtualBox / Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization, etc. Unfortunately, this may not always work perfectly, as each VM technology seems to use slightly different OVA/OVF implementations that aren’t entirely compatible. For example, the auto-deploy feature and the path of auto-mount shared folders between host and guest which are used in the EDGE VMware image may not be compatible with other VM technologies (or may need advanced tweaks). Therefore, we highly recommended using VMware Workstation Player which is free for non-commercial, personal and home use. The EDGE databases are not included in the image. You will need to download and mount the databases, input and output directories after you launch the VM. Below are instructions to run EDGE VM on your local server:
- Install VMware Workstation player .
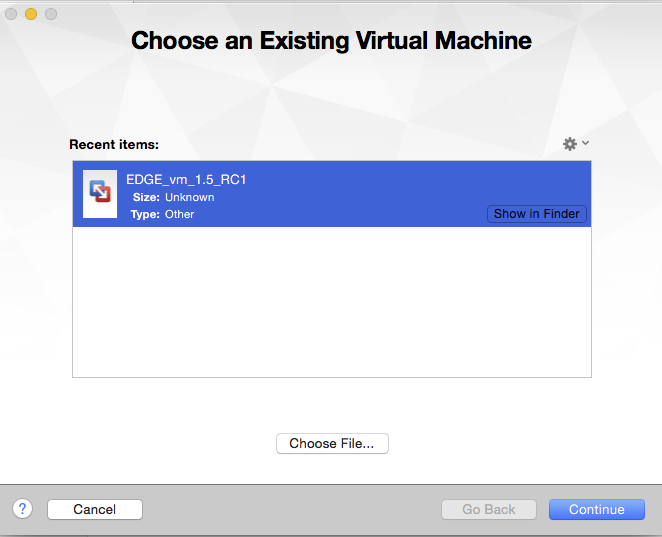
- Download the EDGE VM image (EDGE_vm_dev_RC2.ova) from LANL FTP site.
- Download the EDGE databases and follow instruction to unpack them.
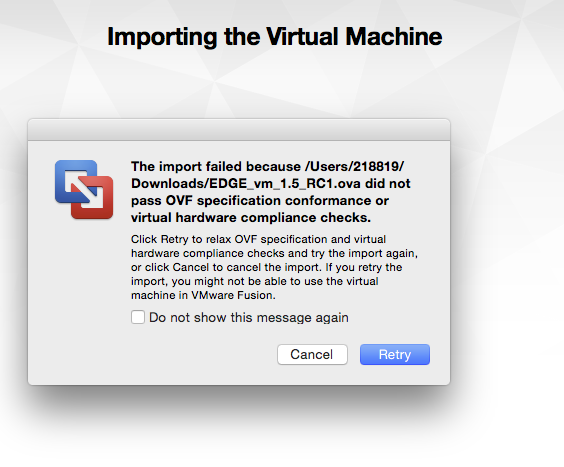
- Import the EDGE VM image. If the first time import fails (due to strict OVF specification), click “Retry”; this will allow import of the image.
- Configure your VM.
- Allocate at least 10GB memory to the VM
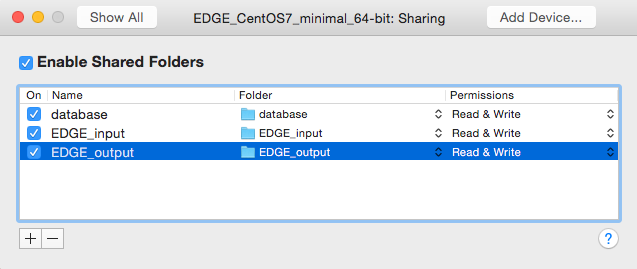
- Share/Mount the database, input and output directory to the “database”, “EDGE_input” and “EDGE_output” directory in the VM guest OS.
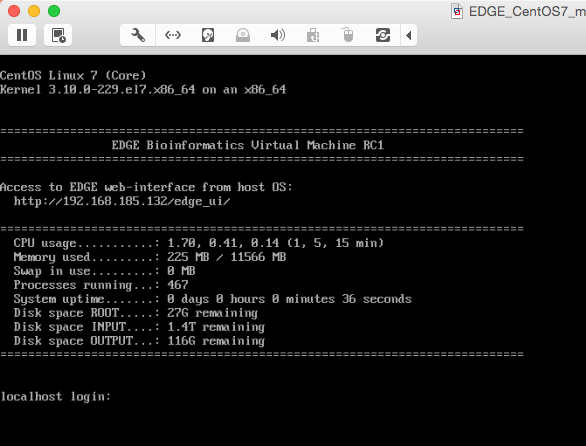
- Start EDGE VM.
- Access EDGE VM using host browser (http://<IP_OF_VM>/edge_ui/).
Note that the IP address will also be provided when the instance starts up.
- Control EDGE VM with default credentials
- OS Login: edge/edge
- EDGE user: admin@my.edge/admin
- MariaDB root: root/edge